Complete Guide for Build an MVP (Minimum Viable Product)
Rahul Motwani
December 26, 2022 572 Views
Quick Summary : What does mean by minimum viable product? Does it work as software or just simple prototype model of a product? Here step by step guide for building minimum viable product. Read till the end to get why MVP, example of MVP, mistakes should avoid and steps to build MVP
The minimum viable product is a basic version of the app with limited functionality. The goal is to solve the user’s core problem. The whole goal of a Minimum Viable Product is to create the minimum set of product features with as little time and investment as possible. This allows you to learn as much about authenticated users as possible. This initial feedback is valuable because it shows your team what bugs and user needs are and will confirm the basic assumptions of the project. Working with MVP is constantly iterative because we have to make many changes and iterations based on the collected user data.
What is a Minimum Viable Product (MVP)?

A minimum Viable Product (MVP) is a concept from a lean startup that emphasizes the impact of learning in developing new products. This validated learning comes in the form of whether or not customers will actually buy your product. The goal is to test your idea or app on mobile or the web without spending a lot of money building a full-featured product. When startups develop an MVP, they focus on getting the product to market as quickly as possible with the minimum features and functionality
The key principle behind the concept of MVP is that you create the product you can offer to clients and observe the behavior that occurs with the product or service. Looking at what people do about a product is more believable than asking people what they would do.
What are Examples of the Minimum Viable Product?
Some of the examples of the MVP are given by,
Airbnb
Airbnb started as a simple website back in 2007 when Brian Chesky and Joe Gebbia were having trouble paying rent in San Francisco. It was a picture of their residence, and soon they had three guests. The concept has been proven, and the platform has been redesigned. But also gives a list of restaurants, Activities in the destination city for users with suggestions and ratings. To build an app like airbnb you need to emphisais your goal with application build cost airbnb.
Foursquare
Foursquare, as a standout solo MVP in 2009, Foursquare is a location-based social network. It previously allowed users to check in from different locations. There are no special functions or complicated designs. There are only games that get people excited about using the service. This has made the product more and more popular, and as you know, Foursquare is now a comprehensive city guide used worldwide to find hotels, restaurants, entertainment venues, and more.
Uber
In 2008, Garrett Camp and Travis Kalanick were frustrated by San Francisco’s sky-high taxi prices and the lack of affordable alternatives. Their original idea was to pair drivers who wanted to pick up passengers with those who wanted a ride. Uber-MVP When it launched in 2009, the ‘Uber Cab’ MVP app was only available on the iPhone or via SMS and was only available in San Francisco. Ride-sharing offers its MVP marketplace, allowing them to test the biggest risks a business faces at a fraction of the cost. The app’s data helped Uber quickly scale and become one of the most valuable companies in Silicon Valley.
Plai
Plai is an advertising tool built for small teams and creators to launch professional ads. Plai doesn’t just make advertising easier. But it also makes it better! In seconds, anyone can promote their brand and products with as little as $1 a day. Plai will take care of it all for you with a few taps. When creating an ad, you can combine graphics, ad copy, targeting, and more for Plai to A/B testing and improve your results over time.
Youtube and Instagram
Instagram and Youtube MVP allow users to share photos and apply filters. Initially, it allowed founder Kevin Systrom to see if the market accepted the product. Users love this application, and since then, all the amazing features we see today, like messaging. Business profiles, stories, broadcasts, tagging, hashtags, and more are all part of Instagram’s incredible success story.
Pinterest is a social network that enables users to share images and discover new interests by posting (called “pinning”) images or videos to their own or others’ boards and browsing what other users have pinned. The social network focuses on the concept of a person’s lifestyle using visual orientation. It enables you to share your tastes and interests with others and discover like-minded people. The social network focuses on a person’s lifestyle using visual orientation. It enables you to share your tastes and interests with others and discover like-minded people.
The popular social networking site Facebook was founded by Mark Zuckerberg in 2004. The basic MVP idea was to connect Harvard students when using the platform. Users can post messages on the board, and the idea became popular enough to expand the platform with more sophisticated features; eventually, Mark evolved Facebook into what we know it today.
Spotify
Back in 2006, the music industry was facing a huge challenge. Several similar music streaming services launched during this time. They spent all their money before realizing customers didn’t want what they had to offer. So Ek and Lorentzon did something smart: They created MVP in the form of a desktop app that offered features. Later, they added an option for customers to pay a monthly fee for an ad-free experience. This path allows them to try out their ideas while mastering their investments.
Spotify’s MVP initially runs in closed beta to test the market and keep costs to a minimum. This approach confirms that the Spotify concept can be a success.
Amazon
A highly customizable, multi-page, personal-recognized shopping destination is one of the most successful examples of minimum viable products that make it big. Although few people know that Amazon used to start as an online bookstore in the early 1990s, at that time, people didn’t trust the internet, and having an online store with ‘everything’ was impossible. The first phase of development consists of improving the top 20 products that can be marketed effectively on the Internet. It was limited to five items, but Bezos eventually became the most marketed online product on books. While most entrepreneurs would invest in a fully functional store, Bezos went frugal and tested his ideas through a simple website (MVP).
Groupon
Founded in 2008, Groupon is a gradual MVP promoting services offered by local businesses and offering limited-time deals through a simple WordPress website. If visitors want to take advantage of a few coupons, they will sign up, and Gropoun’s team will send them coupons in PDF format. Groupon quickly compiles an email list of customers who engage with the site and gets the information needed to create the full Groupon website that it currently has, which is a highly successful platform that operates globally.
When Apple launched iTunes in 2001, the Odeo podcast business knew they were in trouble. Their entire business model is under threat. And they know they can’t compete. While other podcasting companies doubled their growth and made good money after a terrible attempt to gain market share, Odeo thought outside the box and launched a hackathon. Odeo knew that trying to protect Apple was fighting a loss. So they use hackathons to generate new ideas. One of which is a cool SMS messaging service called ‘Twitter’.
Dropbox (Video)
Dropbox is an excellent file-hosting service founded in 2007 by MIT students Drew Houston and Arash Ferdowsi. They realized that building the actual hardware infrastructure was incredibly time-consuming and expensive. So they followed a scaled-down approach to test ideas and created a simple video (as MVP) that tells prospective investors what the product can deliver to customers once it’s built and launched.
The Difference Between an MVP and a Fully-Featured Product

Complex and innovative products often go through all product development stages, from POC to prototype to MVP. Each stage has additional and unique advantages. The whole process helps you avoid common product mistakes, from faulty features, to products no one wants to use.
Both MVP and prototyping are product development approaches designed to validate hypotheses. However, there are fundamental differences between them. Prototypes are developed before the minimum viable product (MVP). Prototypes are not products. It’s just a visual representation of the product, while the MVP is a functional product. You need to prototype when there are aspects of the system that you don’t fully understand or when your concern is a possibility.
If you are sure your idea is feasible, you can create a minimum viable product (MVP) to enter the market to be evaluated by users. This is often a stakeholder, and some potential customers can create an MVP for a large group of customers – your target audience.
Proof of Concept vs. Minimum Viable Product
A proof of concept, or proof of principle, is often an internal project that helps you verify that your theory has real-world applications, especially when developing B2B applications in your proof-of-concept testing.
On the other hand, a minimum viable product allows you to learn how to make that product in the most sustainable way with the least amount of effort. You will learn how people react to different iterations of your product and its potential features. The MVP process allows you to pinpoint exactly what your customers want. So you can only add the necessary features to make it marketable.
What is the difference between a proof of concept and a minimum viable product? They serve different purposes. A PoC provides a theoretical basis for the concept of a particular solution or function. At the same time, the MVP implements feature designed at the PoC and prototype stages.
PoC vs. MVP is like drafting an idea and making an idea come true. The proof of concept outlines the technology for the solution and explores the concept’s potential risks and technical problems. It is intended for analyzing the potential market demand for the product. On the other hand, MVPs are created with the primary goal of examining how customers react to solutions.
Types of MVP
The types of MVPs are given by,
Flintstone’s MVP
The Wizard of Oz (some call it Flintstone MVP); the two names for this type of minimum potential product refer to the working principle. Just as the Flintstones wanted to create the illusion that they actually had cars And the Wizard of Oz uses tricks to pretend to be a giant greenhead, fairy, fireball, or monster, MVPs of this type seem to work perfectly. Startups do all the work themselves instead of using software systems or hiring a team if necessary. There is no basic software at all. It’s a product concept that needs to be reviewed.
Concierge MVP
MVP Facilitator Tests a service concept without building a full service. Instead of creating an app, your MVP lets you create workout recommendations for each client. You will just as easily prove your need to create an app for android phone that will give you the same advice. If you have created a concierge service for your MVP, you should be transparent that it’s currently not an automated service.
Piecemeal MVP
Piecemeal MVPs are a little more difficult to define because there are endless variations. Essentially, piecemeal MVPs are nothing more than merging an existing suite of products to form the foundation of a new service. There are an almost unlimited number of digital tools that allow users to interact with all sorts of things.
Single-featured MVP
Single-feature applications are best used after you have researched your target market and the problem you want to solve. Your goal is to have a clear focus on the app to test your hypothesis. This type of MVP gets you to market faster (and cheaper) than developing full-featured applications. The goal is to get it to market so you can get real feedback from real potential customers about your idea.
Advantages of Starting with an MVP
When an entrepreneur launches a startup, they can guess how consumers will perceive the product. All are based on the assumption that customers have specific needs, and future products will solve that problem in a way that users like.
1. Quick Load
Building a full-featured software application takes a long time and requires a large budget. Depending on their complexity, projects can take years and hundreds of thousands of dollars. MVP versions can be launched much faster without much financial commitment. For example, you are building a product that actually works can take anywhere from 3 weeks to 3 months. You are spending your money wisely. Avoid spending too much on your budget.
2. Low Chance for Errors
Another benefit of the MVP is the ability to expand development for better after MVP release and get real feedback. You can clearly see what changes need to be made. Developers can further refine the features offered by MVP and iterate by adding functions for new use cases based on feedback from early users. You can scale products to a wider audience through continuous improvements based on previous customer experiences. All these benefits, one way or another, optimize MVP development costs and gain valuable insights for creating a product that perfectly fits consumer expectations. It is something that every startup pays attention to.
3. Budget Friendliness
The mature product on the market is the result of many years of the development process. With a competitive price tag, however, as companies repeatedly build these applications over extended periods of time, the overall cost, therefore, spreads over time. By getting more users and gathering more insights to get the product in the right direction through MVPs, they can nurture and facilitate smarter investments.
More opportunities for growth
Similar to market audits, MVPs provide in-depth insights into your target audience. Sometimes a product is popular among users who weren’t initially considered the target audience. Only the user’s interaction with the actual product reveals all potential consumer categories. After identifying your MVP users, you can learn the behavior and needs of your target audience. The continued long-term success of your product depends on how well you know your customers.
A chance to find investors and raise funding
There is no more valuable insight for further improvement than the insights provided by real users. MVP provides the ability to collect early user feedback to help focus on continuous improvement based on user needs. You can listen to your customers and create exactly the products they want.
Even MVPs are released without actual development, such as MVP piecemeal or pre-order. You, too, can gather a wealth of insights for building future products. The sooner you connect with real customers, the better. The more efficient you are at developing. After launching the MVP, the company can analyze which customer groups are the most active. Based on this, it is easier to set the correct priorities for further mobile app development. The startup will not suffer huge financial losses. There will be an opportunity to recover after making necessary changes to the product.
A clearer focus on what is important
Today, many businesses rely on buying from investors to finance new products. The importance of this buy-in is to build confidence in your product offering and the ability to recognize the results you are looking for. By developing an MVP, you can better secure this buy-in. There are many business benefits of an MVP by facilitating businesses to understand whether their idea will work or not before going to investors.
A successful MVP not only proves the viability and usefulness of the product. It also offers tangible solutions to stakeholders who are aware of the return on investment and make the fundraising process easier.
Establishment of a customer base
If you want to attract investors to your organization, there is no better way to use an MVP than to showcase the benefits of the product and customer interest. With the help of MVP, You can validate your business idea before going to investors. It is much easier to attract third-party funding that has a solid business idea with proven market demand.
MVPs are functional products that can be seen by investors because investors have too many capital requests. The minimum viable product will increase your chances of investing in your product. The MVP should come with a business plan and marketing strategy to increase investment interest when comparing two apps for the same purpose. Users will choose apps that provide the shortest path to the desired results. In this respect, some MVPs have been able to beat larger and more mature competitors.
Stats Emphasizing the Need to Build an MVP
- 29% of startups fail because they run out of cash.
- Properly scalable startups grow 20 times faster than startups that expand early.
These statistics clearly show the benefits of starting a new product development process with an MVP. However, there are more reasons MVP product development companies have to create minimum viable products.
It creates an initial model that provides a starting point for discussion and presents a clear reference point. The preliminary concept approval process includes sharing the model with potential customers and testing it with real users. This helps in understanding potential problems with the product.
Starting the actual build process after spending months refining and refining software concepts is an important and inspiring step in building a full-fledged product.
How to validate your Idea for MVP
Customer reviews are the most direct way to get MVP-specific reviews. There are real reviews from people who will use the product. Conduct interviews with potential customers. Listening to any issues they raise will provide valuable insight.
Concierge or fake door MVP
In many ways, the concierge method is similar to the do-it-yourself approach, except that instead of counterfeiting a functional product or service. You will know in advance about doing manual work and even go the extra mile by delivering products efficiently. A customized services for a number of clients – hence the name “Concierge.”
A prime example of this approach is being used by a company called Rent the Runway, an online costume rental business. They provide one-on-one services to key demographics. This method is not only successful in spreading the word about the business and giving them valuable feedback. But it also examines their most important uncertainty: Will the woman rent the dress?
When you use this method to create a Concierge MVP, instead of devoting time, money, and resources to building an actual product, you will find answers to your most important questions first. That is, are you creating something that customers will actually pay for?
No-code / low-code solutions
You cannot know if your application will succeed until you actually launch it. Does this mean you should invest in full development? Absolutely not the no-code, low-code MVP (minimum viable product) development approach allows you to validate your idea without investing in a skilled development team (and expensive) and a stack of advanced techniques.
With an MVP, you can test your product ideas more cost-effectively and faster than building a full-fledged software product. This tool facilitates the process with visual programming and reusable components. And according to 2019 research from Forrester Consulting, these technologies are now a viable alternative to custom coding for 31% of IT companies.
However, this approach requires careful planning and an understanding of its limitations. It will show you how to make your MVP as low-code as cost-effectively as possible and avoid common mistakes that companies make during development.
How to Create a Roadmap for MVP?

Did you know that 90% of startups fail? There are a few related factors that cause this to happen. These factors include running out of money. Entering the wrong market and research is inadequate. However, the risk can be minimized by using the MVP development process.
All product development begins with general assumptions about potential users and their actions. Following the step-by-step instructions for the Minimum Viable Product development process gives you the opportunity to validate those assumptions. It is a process of creating temples and repeatedly learning to check expectations to help ensure things are continually improving.
You build a basic version of the product that includes core functionality and delivers it to target users. Following this, you gather feedback to learn about the people who use the product. Once again, this learning feeds into an iterative model that aids in the decision-making process. This step is crucial in helping you decide which areas of the product you should focus on in the next phase of the product lifecycle.
- The main benefit of the minimum viable product is that it allows you to quickly realize the value of the product and verify the validity of various theories. However, this framework has some additional immediate benefits as well.
- Increase the chances of success of the product in the early stages of development. This helps to increase the confidence of stakeholders/investors.
- You can reorient your product’s business based on your audience’s response to your MVP through user value.
- You can see if the market has been reviewed for your product.
- It can help you formulate a strategy to monetize your products.
- It is ideal for reducing development costs compared to launching full-featured products with high costs and years of development.
- Although we don’t just take our word for it, Dropbox is a great example of how to leverage the use of MVP and use it to determine success. As a result, they have progressed to a widely successful organization with a net worth of $12 billion.
How to build a Minimum Viable Product?
MVP product development is not significantly different from typical software product development. But the speed and aim are different.

MVP Building Basic Goals
- Product viability test: If you want to check if your idea is effective? But don’t know where to start?
- Spend less money on product development.
- It is faster product delivery that solves at least one user problem.
Step 1: Start with Market Research
Market research is a fundamental aspect of any successful project. If you don’t want to end up with failures, Analyze and make sure you create an attractive and useful MVP website or app for users. There are a number of additional platforms that offer paid surveys, such as Swagbucks, OnePoll, Toluna, etc. These platforms will help you build a detailed picture of your customers. Moreover, watch out for your competitors and carefully examine how they create the minimum viable product.
Step 2: Ideate on Value Addition
You must understand how to create an MVP because every business owner should analyze their project. By answering the following questions:
- What problems can my platform solve?
- Is it useful to consumers, and how?
- Why do they use this solution?
If all responses are found, you will have a clear idea of the main product quality. After identifying problems and bugs, you have got all the updates (and solutions); you can start creating MVP versions of your future products.
Step 3: Map Out User Flow
Once you have done your market research, take into account the strengths and weaknesses of your potential competitors. You should validate your concept before entering the minimum possible product development stage. One of the most cost-effective and time-saving ways is to create a prototype before you create an MVP. That way, you can see what your future product will look like.
Step 4: Prioritize MVP Features
By the time you conduct market research taking into account the user problems that need to be solved; you can switch to select the minimum applicable product software features that are most valuable to customers after creating a user flow in which you specify your attributes. Products should have and prioritized them in order of importance.
Step 5: Launch MVP
After all the criteria have been handled, you can start building your MVP, so how to create a minimum viable product that will be lucrative and attractive both for users and investors. Remember: You should use happy mediums to get hands-on products. Your professional and concise MVP shouldn’t be overly active and at the same time, it should be quality. All shortcomings are fixed in a timely manner to avoid failure from the start. It must also attract customers with their ease and solve their underlying problems. Finally, you can launch the MVP.
Step 6: Exercise ‘B.M.L.’ – Build, Measure, Learn
When you reach the development stage, you continue the MVP development process with the help of the Lean Startup methodology known as Build-Measure-Learn (BML). There are several ways to collect user feedback data for your MVPs. One of the best ways is to interview and survey your first users – users who were interested in the product at the concept review stage while they are looking for some solutions that you are ready to serve.
10 Development Mistakes to Avoid While Building an MVP
New products are launched by companies of all sizes. Even established companies constantly launch new products. Even if a startup company has a small budget but large companies can spend money on product development. Many companies end up putting too much effort into over-engineering products. Doing so leads to a huge loss of time, effort, and money.
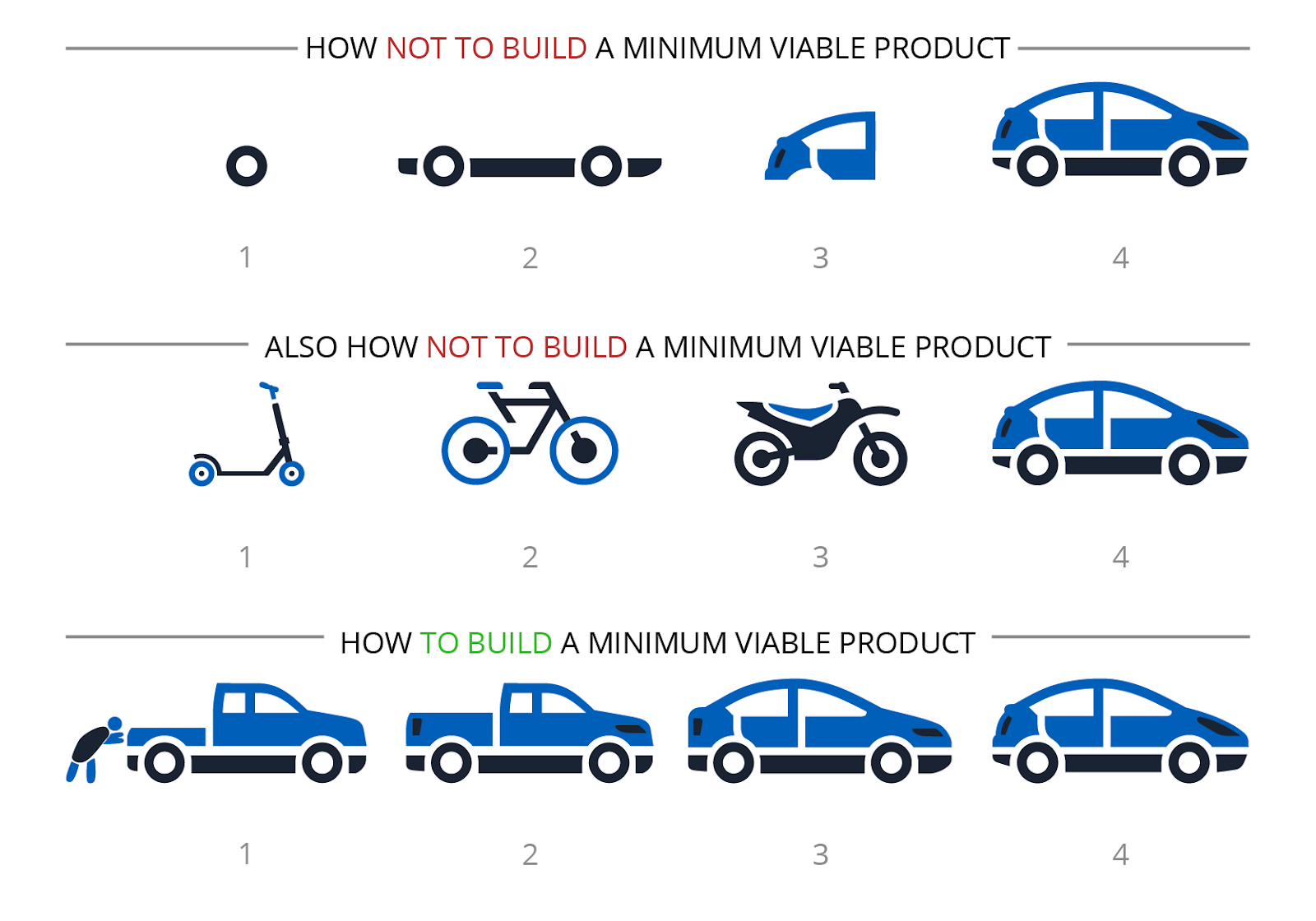
Source:- https://prismic.io/
1. Choosing the Wrong Problem to Solve
Your product will stand out in the market based on key attributes. You will need to design a product roadmap to launch products periodically. Your entry-level product doesn’t have to be groundbreaking. But it should connect with your potential customers.
2. Skipping the Prototype Phase
Every product is created according to the specific characteristics of the buyer. Those under the buyer specifics should be allowed to run in MVP. But it can be a small high-quality audience for which comments will be meaningful. Giving to a large and diluted audience yields a lot of incoherent feedback about MVPs, leading to a product roadmap that goes wrong.
3. Targeting the Wrong Segment of Persona
On the other hand, you need to understand that your customers solve the same problem using different custom software development. Customers will use the techniques themselves or use the solutions of your competitors. You need to keep this in mind when you are bringing out an MVP. Keeping your MVP too simple won’t make your buyers even start testing products. This will reduce MVP adoption by potential customers. You will get false negatives about the potential of the product itself.
4. No market need
Many startups don’t spend time and effort on market research. The lack of interest in the research came about because the initial idea was the only stream that could monetize it. There is an urgency to bring the product to the market, and they should finish the MVP. However, the funds available are minimal. So startups end up analyzing the competition in only a few products. Startups don’t talk to customers much. Many times owners are convinced that they have identified a gap in the market that no one has yet filled. Many companies are following this trend.
5. No clear goal
Startups have few resources in terms of capital, brands, and people, so organizations can’t hire people who specialize in technologies, domains, and products that have been built in the past. Therefore, it is essential to bring in outsiders with complementary skills that the existing team does not have. Outsource the right mentors and development partners will help fill the domain and technology gaps that current teams will have. This mix of multi-skilled teams will help to develop a better MVP that first-time users will love.
6. No budget for marketing/poor marketing
Think of your product strategy as a tool of your organization. It is a mechanism that is supposed to turn the resources you invest into tangible results. You won’t get very far if your engine isn’t running well. Although many entrepreneurs think running out of cash is their biggest concern. Suppose you can prove that your product works, although not yet breaking any world records. If you need to, however, things get more complicated when your strategy lags behind.
7. Costly/Cheap team of developers
It’s tempting to think that the more developers you have, the better. The faster you drop the MVP; however, this couldn’t be further from the truth. While acquiring a specialty may be good in the short term, getting a team too big too quickly can hamper the long-term success of the project.
8. The Importance of Feedback in Building an MVP
MVP is considered to be the most critical and important step in the entire development process. Companies tend to have conditional projections and expectations on their projects. However, they all remain theoretical in reference to similar competing products. Until gaining transparency and stability with real data, and this is where MVP comes into the picture.
MVP allows full product testing in the most basic version in real market situations. It allows you to try, experiment, and understand the engagement of the product with the target audience. It also helps to measure user interactions, paying particular attention to their ultimate wants and needs.
Essentially, an MVP provides a clear indication of what works and what doesn’t work on a product. Most importantly, what can be improved?
MVPs determine the direction of product development in a specific way. And finally, it will help explain the vision of the product. When you launch the first version of MVP, you will learn about the real user experience. And you can’t achieve that through internal testing or research exercises, so putting your product on the market as an MVP version gives your team the opportunity to learn in-depth about your product and use the feedback received from users to improve and improve upcoming product releases.
The MVP nature is more suited to iterative processes than linear ones. Give your team a platform to learn and implement iterative development processes like Agile, which can add value to your product during development.
9. Inappropriate Development Method
Developing a successful MVP is like cooking. If you intend to marinate and roast the chicken, then change your mind and decide to boil. It will spoil and fail. This is why some MVP developers abandon the project halfway.
There are basically two ways to create an MVP: Agile and Waterfall. Agile software development is more efficient in this scenario compared to Waterfall (traditional method) due to its ability to deliver high-quality results weekly.
Although the payment structure may not matter but it is worth noting that most companies offering agile software development are paid per hour While companies using Waterfall are paid based on bids. When developing using a waterfall, you may end up with a product that meets specifications instead of really essential products. Each change made beyond the agreed scope may be subject to an additional payment. This can affect the development process where payments cannot be made on time, thus delaying the MVP or affecting the developer relationship.
10. Confusion between Qualitative and Quantitative Feedback
One of the main objectives of an MVP is to generate feedback to make the final product better. Ignoring feedback renders the entire process useless as it lacks purpose. Why create an MVP just to ignore the suggestion later?
Feedback is important because it helps you understand your users better. Personalize your products to meet your customers’ needs. As well as assessing the audience’s perception of your product, ignoring user analytics and opinions is business suicide.
Tips to Target the Right Market while Building an MVP
1. Analyze the Competition
It is important to delve into competitor research to determine what products will compete with. It’s almost impossible to create an MVP that doesn’t exist in the market. Although startups have unique ideas but it still joins an existing and competitive industry. So they have to find a way to place a minimum viable product in an industry where competitors are doing what they are trying to do.
To know this, Startups must study competitor information to evaluate their strengths and weaknesses. Please find out your target audience and what they offer. Startups can move forward in the same target markets that their competitors have chosen or can focus on groups that competitors may overlook.
2. Geographically Segment the Customer Base
Once a startup has found a suitable customer base for an MVP, the next task is to focus on geographic segmentation. This is an effective strategy used by businesses and used to familiarize you with location-based attributes that comprise specific target markets. Analyzing the location of your ideal customer base can be a real game changer while on the path to building an MVP. For example, what is the purpose of starting a search from Southern California? If the minimum possible product is a winter jacket, winters here range from moderate to warm.
3. Find the Motivation behind a Purchase
After segmenting the customer base by geography, the next task is to understand the motivation behind the purchase. This will help startups strike the perfect balance between MVP positions. The easiest way to achieve this is through surveys. Take into account the minimum viable product. Ask relevant questions that surround the points. When the survey is ready, this can be done in several ways depending on the budget.
4. When you should release your MVP?
You can follow the below steps before release your MVP.
1. Monitor and maintain
You will need a list of business assumptions to track the dynamics of your MVP after launch. It helps to make the right decisions. You can set a limited number of properties for every iteration to keep the process simple and efficient.
2. Collect and analyze reviews
The main idea of being a startup and launching an MVP is quickly taking the market. Startups have the right to make changes as many times as they like. Founders need to create a culture that is flexible and innovative to achieve agility. You can also analyze the reviews.
3. Get ready for change
These goals should be specific, measurable, achievable, and timely. This complex helps you move from one milestone to another without distraction.
4: Work on pricing
The name, brand, logo, or colors of a startup don’t mean much in the early stages of development. Profit is the only metric that represents the potential of your product in the market. So you can set your budget.
5: Invest in marketing
The main rule of product launch is that users should love your product, not you. You should work with users. If they pay once, continue the strategy and encourage them to invite their friends to sign up too.
Measuring Success after Building an MVP
There are many ways to predict the future success of a product accurately. Here are some common, effective, and proven ways to measure MVP success:
1. Word of Mouth
Traffic is a valuable metric in predicting success. Another way to track success is to interview prospects. Start by identifying the problems customers are facing or are likely to face and ask what they think.
2. Engagement
Participation enables startups to measure not only the present value of their products but also their future value. Engagement improves the user experience based on feedback.
3. Sign-Up
Signing up is a possible way to measure user interest. It may also convert into revenue based on product interest measurements.
4. Better Client Appraisals Based on the Feedback
The number of downloads and launch rates shows user interest in the app. The lighter the app, the more it will be downloaded.
5. Percentage of active users
Download and launch rates aren’t the only factors that measure MVP success. It’s important to study user behavior and monitor ratings of active users on a regular basis.
6. Client Acquisition Cost (CAC)
It is necessary to know how much it costs to acquire paying customers. This keeps startups informed about whether their marketing efforts are effective or if changes are needed.
CAC = Money Spent in Traction Channel / Number of Clients Acquired from Channel
7. Number of Paying Users
Know your average revenue per user (ARPU) and track revenue-generating products.
ARPU = Total revenue for the day and age/number of users.
8. Client Lifetime Value (CLV)
CLV shows how much time users spend on an app before uninstalling or quitting it.
CLV = (User Gain *app usage period) – acquisition cost
9. Churn Rate
Churn shows the level or percentage of people who uninstalled or stopped using the app.
Opting out = number of opting out per week or month/number of users at the beginning of the week or month
MVP common myths
There is still a lot of misconception about what an MVP is and what isn’t.
1. MVP is a low-quality product version
This way of thinking can do great damage to you. Production versions of products should have a limited number of features but the quality must be as high as you can. The ultimate goal of an MVP is to attract the first user and suggest your idea and see if the market will respond or not. Low-quality products do not make a good impression by default and waste your efforts. Many unsuccessful products have proven that MVP design is important. These days, the word “works” is often replaced by the word “cute” to emphasize the importance of creating products that people like really use.
2. MVP helps gain first users
From one side, yes, the first user will be your first audience. However, an MVP is not a marketing strategy. It is a development technique that allows developers to create better products based on customer feedback.
MVP is a prototype
Optional; it depends a lot on the nature of your product. Landing pages, mockups, or product demo videos that don’t exist will also work. The goal is to present the essence of the product concept.
Tips for your MVP business idea
This is because many developers and managers use minimal viable product concepts when working on projects. So there are many professionals with their own unique MVP guidelines. It’s definitely not a copy and paste process. There is enough space to make it fit your company’s concept and philosophy, although the core principles are the same for all businesses. But there are some things you can do to make your business unique. For example, Hung Nguyen of Smallpdf recommends that new startups run weekly instead of monthly or quarterly. To better understand the ongoing process.
- Proof of Concept: Before creating an MVP, you should create a proof of concept prototype (POC) to validate your idea.
- Complement the features: When your MVP starts to take shape, Take a moment to narrow down the features as “must have and “add-ons.” Decide what adds the most value for your consumer base. And make sure it leads to a good user experience (UX). Have a success plan, including metrics.
- Unless you set certain goals and parameters, when it comes to product development, you will need to set key performance indicators (KPIs), which will guide you as you build them. Based on the results, you will be able to make informed decisions about what needs further improvement and how to make the most of your time and resources.
- Although this is your minimum viable product but it shouldn’t be sloppy and spotty. The key features should be robust and attractive to the users you are targeting. Even in its most basic form, the pitch should be clear and able to solve the problem.
How Much Does it Cost to Develop a MVP?
Every team or expert will give you a different estimate when it comes to MVP development costs, even if you describe your project the same way. Estimates will still differ because the cost of MVP software depends on various variable factors. The most important include:
- Scope of design and development work
- The necessary technology stack
- Development team type
- Your development company’s hourly payment rate
- Type of contract
As you can see, an MVP for your startup or business will likely cost between $15,000 and $50,000, which is probably around $30,000. Of course, MVP costs can be higher or lower. It depends on the scope of work, the team and the type of contract, etc.
Whether you are a startup or a business, an MVP can help you test your idea before it takes too many features or overruns your budget.
How Groovy Can Help You to Build MVP
For Minimum Products (MVPs), Groovy Web guarantees that you have all the right information, advice, and alternative solutions for creating the perfect product for your customers and their needs. They aim to develop your product with minimal effort and get it fully reviewed and appreciated by the marketplace. Groovy Web can help you validate your idea and make it a reality. They are the top MVP development company that lets you build user-friendly, reliable, high-performance applications and are scalable. You have come to the right place if you are looking for a trusted MVP development team to help you build your project from idea to finished product.
Wrap-up
Although it may seem grand, an MVP is only step 1 on your initial journey. It allows you to validate ideas cheaply and quickly. Get feedback from real users, and there is proof that your idea works for stakeholders and investors. This guide will help you to know the MVP creation process and emphasize the importance of problem definition, market research, prototyping, and collecting suggestions.
All great things start from small beginnings. So you don’t have to create a full-fledged product to win the market. You can create an MVP, test the feasibility of your business idea, and replicate it.
Written by: Rahul Motwani
Rahul Motwani is an experienced Project Manager with a demonstrated history of working in the information technology and services industry. He started his career as a Backend developer and currently has his hands-on managing projects at Groovy Web. He is a strong program and project management professional with a Bachelor's degree focused on Computer Application.
Frequently Asked Questions
We hope these clear your doubts, but if you still have any questions, then feel free to write us on hello@groovyweb.coHow to recruit customers for your minimum viable product?
- You need to they had a problem
- Know they have a problem and are willing to fix it
- Knowing that they have problems and are unwilling to fix
- Already using the free version of the solution
- Already paid for the solution and not satisfied with the solution
What is the difference between a prototype and a Minimum Viable Product?
Prototyping is a quick way to test the basic ideas and assumptions of a product. MVP, on the other hand, is a working version of a product that contains only the core features. Ideal for testing resulting in valuable feedback and information, But it takes the least amount of time and investment in this process.
How long should it take to build an MVP?
MVP generation is based on a set of properties, design complexity, and human resources involved in the process only. It usually takes about 3-5 months.
Why is a minimum viable product important?
A minimum viable product, or MVP, is one that has enough features to attract early adopters and validate a product idea early in the product development cycle. In industries like MVP software, it can help product teams get feedback from users as quickly as possible to iterate and improve products.
What is the goal of a minimum viable product?
The MVP's goal is to verify the proof of the product. It Tests hypotheses about market demand, Changes the vision of the product, and prioritizes where to invest in future developments.
Related Blog

Rahul Motwani
The Road to Growth: Guide to Scaling Your Software Development Team
Software Development 27 Jun 2023 15 min read
Nauman Pathan
Why Cloud Computing Is Important for Your Business
Software Development 02 Feb 2023 17 min read
Sagar Patel
Software As a Service: Step by Step guide to Build SaaS Product
Software Development 01 Feb 2023 18 min readSign up for the free Newsletter
For exclusive strategies not found on the blog

